Business Use Cases for Mixing CRMs and Mobile Apps
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) dashboards and interfaces are traditionally optimized for desktop usage, standard for business software.
After all, 99% of CRM users are dedicated employees.

However, as covered in our guide to custom Customer Relationship Management development, every CRM serves three core business functions:
- Customer Service
- Marketing
- Sales
All features in a custom CRM must link back to these functions, including platforms served.
So if you have good reason to believe the unique benefits of mobile apps can improve how well your business can serve clients, market your products, or generate sales, a custom CRM for mobile usage is worth exploring.
Below, we provide a breakdown of the process to help you decide.
Unique Advantages of Mobile Apps

There four main benefits of mobile apps:
- On-the-go access: Allows users to access the app much more frequently
- More user-to-user interaction: Allows
- Push notifications
- Better access to phone hardware
If you’d like to learn more, we explain them in our guide to mobile app business perks, but for now, you just need to know your CRM users will make use of these advantages.

For example, if your CRM was available as a full fledged mobile app, would your users…
- Use it productively outside of the office or home, such as on the train?
- Reply to messages and tags by other users more frequently?
- Use their phone cameras or GPS to directly update the CRM database?
As we’ll explain at the end of this guide, it’s not enough to think, you need to know!
That said, let’s see how much to budget if you engaged for a custom CRM mobile app 🙂
Overview of Custom CRM Mobile App Development
We’ve kept our estimates conservative and erred on the higher side of things.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Development | USD115,000 |
| MVP Development | USD35,000 |
| Total Development Time | 12 months |
| Time to MVP | 16 weeks |
| Maintenance Cost | USD3,000 / month (excl. 3rd party tools) |
This assumes three very important things:
- A single cross-platform codebase for Android and iOS phones
- A single UI / dashboard prioritising mobile use
- No scope creep or significant changes to requirements
We’ll discuss these in more detail after laying out the main development steps.
First-off, let’s clarify what it means to stuff an entire CRM into a phone!
Breaking Down a Typical CRM
Let’s look at the separate apps in a conventional desktop-based CRM and their key features.
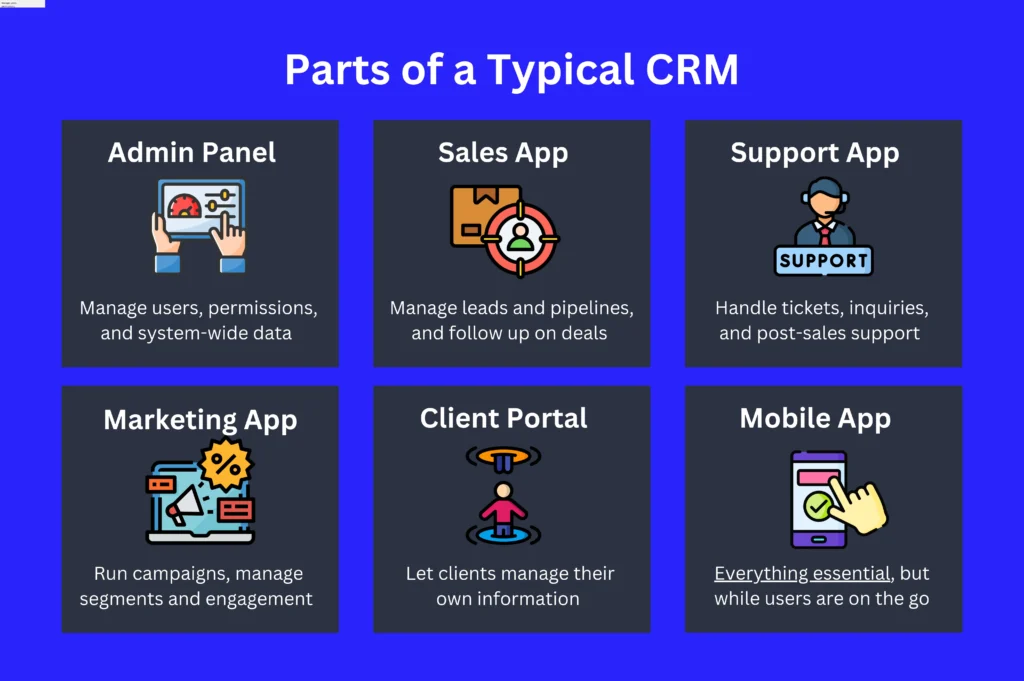
As you plan your custom mobile CRM, keep these functions in mind, and feel free to add others that you need, especially if they’re industry-specific.
Also, note even a typical CRM has a mobile app as an add-on to the main desktop version.
We want to say all mainstream CRM solutions provide this.
But that’s just it–their CRM mobile apps are add-ons to proven desktop-based ecosystems.
Specifically, they are simplified versions of the desktop CRM, especially interfaces.
Of course, just because most CRM solutions use mobile apps as a simplified version of their desktop app, doesn’t mean you have to.
Determining Your CRM Mobile App Needs
The first question to ask is: Will your CRM mobile app serve as…
- A secondary tool that complements a primary desktop version?
- Or the primary and only CRM tool for your organisation?
First scenario? No problemo.
The second scenario? Potential problemo.
This means you’ll need to balance functionality with clean, intuitive mobile UX.
If you’re thinking of a Salesforce level CRM, it’s probably not going to happen on mobile, but a leaner and stripped-down CRM is achievable.
The second consideration: What kind of customization do you need most?
Examples include:
- Custom integrations with third-party software or internal databases
- Industry-specific workflows
- A bare-bones, super lean CRM
- A specific feature unique to your business process

Based on the users and apps we listed above, here’s a table to help you determine what features your app needs and where the customization should happen.
| User & Purpose | Common Features | What’s Missing? |
| System Admins – Manage users, permissions, settings, and system data | – User management – Custom field configuration – Audit logs and usage reports – Workflow / automation builder – Data import/export | |
| Sales Team Members – Track leads, manage pipelines, follow up on deals | – Lead/contact/deal management – Pipeline view (Kanban or list) – Reminders & tasks – Email/call logging – Notes and activity history | |
| Customer Service Members – Handle tickets, customer inquiries, post-sales support | – Ticketing system – Customer contact lookup – Knowledge base integration – Tagging & escalation – Response templates | |
| Marketers – Run email campaigns, manage segments, and track engagement | – Contact segmentation – Email templates and sending – Campaign performance analytics – Drip workflows – Lead scoring | |
| Clients and Leads – Let clients view and manage their own information | – View personal account data – Track support requests – Update contact preferences – Download documents or invoices – Secure messaging |
Based on the table of features above, here is a list of necessary integrations.
| Category | Common Integrations |
| Email & Calendar | Gmail, Outlook 365, Google Calendar |
| Marketing | Mailchimp, SendGrid, ActiveCampaign |
| Sales Tools | Twilio, DocuSign, Typeform |
| Customer Support | Zendesk, Intercom, Help Scout |
| Storage & Docs | Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive |
| Billing & Invoicing | Xero, QuickBooks, Stripe |
| Identity & Security | Okta, Auth0, Google SSO |
Be sure to involve all key stakeholders when determining your requirements, especially team members who will actually be using it!
Our 6 Stages of CRM Mobile App Development
Building a custom CRM means following the typical stages of app development, of which there are six (seven if you include the work done before approaching a developer)..
Stage 0: Prepare Your CRM Mobile App Brief
A brief is a preliminary document that gives developers an idea of your project, namely :
- Problem
- Solution
- High-level Requirements
- Budget Range
- Timeline
- Similar Applications
It gives us context and helps us form clarifying questions when we move to the next stage.
App Brief Template
Download this FREE editable template now to craft your perfect App Brief! Let us know where should we send it through the form below.
Secretly, developers also use it to filter out clients who aren’t serious!
Stage 1: Requirements Gathering
During this phase, we work with you to define the requirements for your CRM.
We typically run our own version of a product roadmapping workshop, where we align on:
- Target Audience
- Problem Statements
- Value Proposition
- Primary Platform
Based on our discussions, we come up with a timeline for all features.
And most importantly, we shortlist essential ones to roll out with the MVP.
Stage 2: UI/UX Design
If your custom CRM compromises on either, employee adoption will always be a challenge.
You’ll constantly hear “Why can’t it be more like [insert popular CRM here]?” complaints.
Our UI/UX designer will ensure your CRM not only looks great (UI) but also delivers a seamless, enjoyable user experience (UX).
Stage 3: Back and Frontend Development
If you’re familiar with Agile methodology, we work in two week Sprints.
During a Sprint, our backend developers build the back-end architecture while the frontend guys turn the designs by the UI/UX team into functional app interfaces.
At the end, we get your approval on progress and align on action items for the next Sprint.
If that sounds like gibberish, here’s a guide to Agile methodology for non-techs!
Stage 4: QA & Testing
The main purpose of this phase is for us to improve the stability of the CRM while minimising bugs that impact the user experience.
There’s no such thing as bug-free software, but that is no reason to compromise the user experience.
Stage 5: Launching Your MVP
We deploy your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to a live environment so employees can begin using the CRM.
As they use it, we’ll be on hand to:
- fix high-priority issues that were initially missed
- monitor how core features perform
- identify unexpected user behaviour
- see where improvements are needed
Stage 6: Iterate & Maintain
Based on how your team responds to the early version of your CRM, we reevaluate the product roadmap together.
More often than not, many features that were initially thought critical turn out to be unnecessary.
Meanwhile, use cases that nobody thought of suddenly reveal themselves.
Ultimately, we align on the development of the rest of the CRM to truly serve your business needs, alongside regular updates, bug fixes, and general maintenance to ensure the parts of the CRM that have been built remain stable.
Timeline of CRM Mobile App MVP

| WEEK | DESIGN | DEVELOPMENT |
| 0 | Kickoff meeting to align on essential features for MVP in 16 weeks | |
| 1 | Initial UI/UX + User Feedback: – Recruit users for usability testing – Produce mid-fi designs – Conduct user testing with designs | Plan Front and Backend: – API Specification – API Controller List – API Service – Database Schema |
| 2 | Complete UI/UX: 1. Iterate designs based on user feedback 2. Begin hi-fi designs | Development Sprint Planning (weekly cycles): (Start of Sprint) 1. Plan work for the coming week 2. Work on, test, and write automated tests for features 3. Submit pull requests for code, UI/UX, and functionality review 4. Update request if changes / improvements required 5. Merge feature and move to next item (End of Sprint) 1. Demo to you and share the link to install / test 2. Plan work for the coming week 3. Repeat steps 2 – 6 Note: Receive designs + code review in Week 5 |
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | Handoff designs to developers | |
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | Development Sprint Planning + QA Testing (weekly cycles): – Thorough QA testing – Security audit – Automated testing | |
| 11 | ||
| 12 | Launch + support / bug fixing | |
| 13 | App + documentation ready for handover to you or your team | |
Almost No Business Needs a Custom CRM Mobile App!
We’re generalizing here, but generalizations exist for a reason.
CRMs are generally desktop-first for two very good reasons:
- They are used for work
- They have very data-heavy displays
Most people don’t want to use their phones for work or look at tons of data on tiny screens.
We’ve experienced many businesses that built custom internal apps that nobody used.
We don’t want you to end up like that, so here are two steps to take if you haven’t.
Confirm a Mobile Website Isn’t Enough
For starters, see our guide to mobile apps vs websites in case the latter is good enough.
If you still think your business needs a mobile CRM, verify this with key stakeholders, especially team members that will be using it.
Conduct User Interviews
If you’re unsure what to ask, the user interview part of our SaaS validation guide can help.
With this you will have the clearest possible idea of your requirements
And if, with that clarity, a custom mobile-first CRM still sounds like the best solution, reach out for an honest assessment.
If you’re looking to build a custom CRM, check out our portfolio of past projects and contact us if you like what you see. Also, consider joining our mailing list for a one-stop resource on everything from SaaS validation to execution and promotion. Get a nifty list of questions to ask app developers when you sign up!
App Developer Interview Questions Template
Download this template now so you know exactly what to ask App Development Agencies! Let us know where should we send it through the form below.



